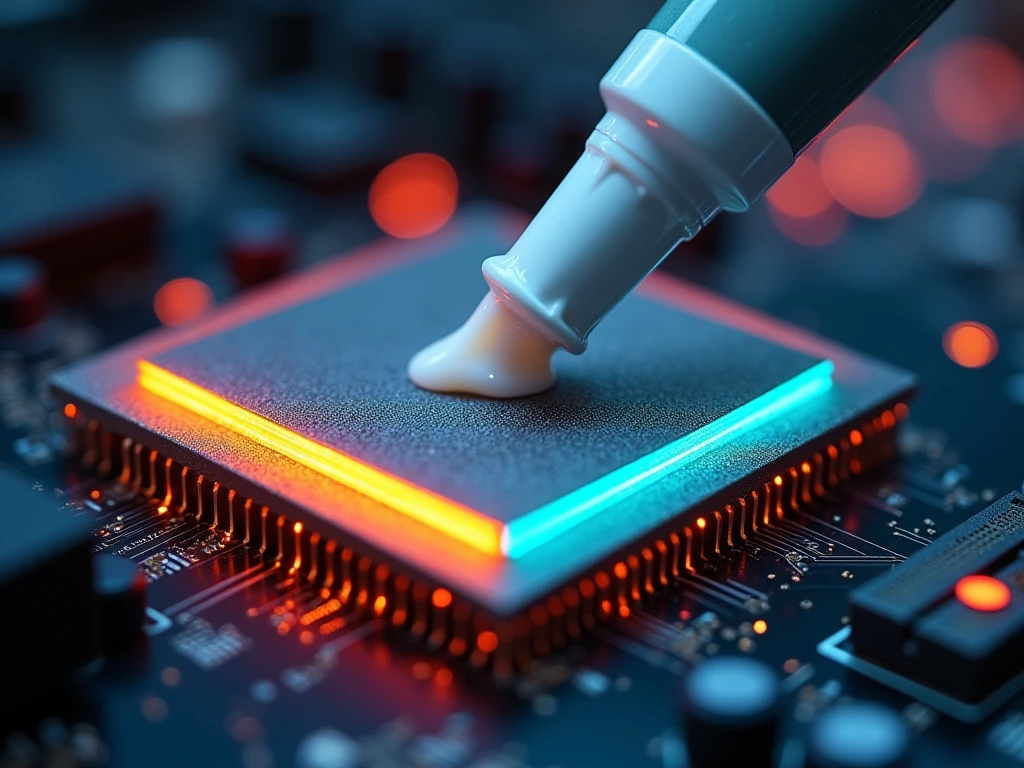
Thermally Conductive Grease, also known as thermal paste or thermal compound, is a thermally conductive material used to improve the heat transfer between a heat-generating component, such as a CPU or GPU, and a heatsink or cooling solution. The purpose of thermal grease is to fill microscopic imperfections or air gaps on the surface of the component and the heatsink, ensuring maximum contact and efficient heat dissipation. Without thermal grease, these air pockets can act as thermal insulators, significantly reducing the cooling efficiency of the device.
Table of Contents
Non-Silicone Thermal Grease
LiPOLY’s N series is a non-silicon thermal grease with a thermal conductivity of 1.3-6.0W/m*K. None low-molecular- weight siloxane volatilization cause no electrical contact failure. It is suitable for optical products or sensitive electronic components. Extremely low thermal resistance and good thermal conductivity have been widely used in thermal control technology for consumer electronics and microprocessors. When the temperature of the component rises, the viscosity of the grease will decrease for wetting the interface components.
See the complete thermal datasheet by visiting: G3380NA/NJ/NK/NT Datasheet

LiPOLY TIM Technology : Thermal Solutions
How Does It Work?
Thermally Conductive Grease is not a heat sink by itself, but it enables the heatsink to perform its function more effectively. When applied between the heat source and the heatsink, the grease spreads out evenly, allowing for better heat conduction due to its higher thermal conductivity compared to air. Thermal grease typically comes in either silicone or non-silicone formulations and may contain additives like metal oxides to enhance thermal performance.
Types of Thermally Conductive Grease
- Silicone-Based Thermal Grease: This type is widely used due to its versatility and durability. It contains silicone oil mixed with fillers like zinc oxide, making it flexible and easy to apply.
- Non-Silicone Thermal Grease: These are often used in applications where silicone contamination is a concern. They tend to have higher thermal conductivity and stability in extreme temperatures, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
Key Uses Benefits
- Enhancing Heat Transfer: Thermal grease fills the microscopic air gaps and imperfections between a heat source (such as a CPU or GPU) and a heat sink. This ensures efficient heat transfer by replacing air, which is a poor conductor of heat, with a material that has much higher thermal conductivity3.
- Preventing Overheating: By improving the thermal interface between components, thermal grease helps prevent overheating, which can lead to system instability, performance degradation, or even hardware damage2.
- Maintaining Device Stability: Proper application of thermal grease ensures that electronic devices operate within safe temperature ranges, thereby enhancing their stability and longevity.
Typical Applications
- CPUs and GPUs: Thermal grease is commonly applied between CPUs or GPUs and their respective cooling solutions to ensure effective heat dissipation.
- Power Electronics: Used in power supplies and motor controls where efficient thermal management is critical to maintaining performance and preventing failure.
- Optical Devices: In applications where silicone contamination must be avoided, non-silicone thermal greases are preferred to prevent interference with sensitive optical components.
Application Techniques
- Even Application: It is crucial to apply thermal grease evenly and in the right amount. Too much grease can act as an insulator rather than a conductor, while too little may not cover all the necessary surfaces.
- Automated Systems: In professional settings, automated dispensing systems can be used to ensure consistent application, minimizing human error and ensuring optimal performance.
In summary, thermal grease is an essential component in modern electronics, ensuring that heat generated by high-performance components is effectively transferred to cooling systems, preventing damage and optimizing device performance.